Which Has the Most Protein Turkey Chicken or Beef

vs

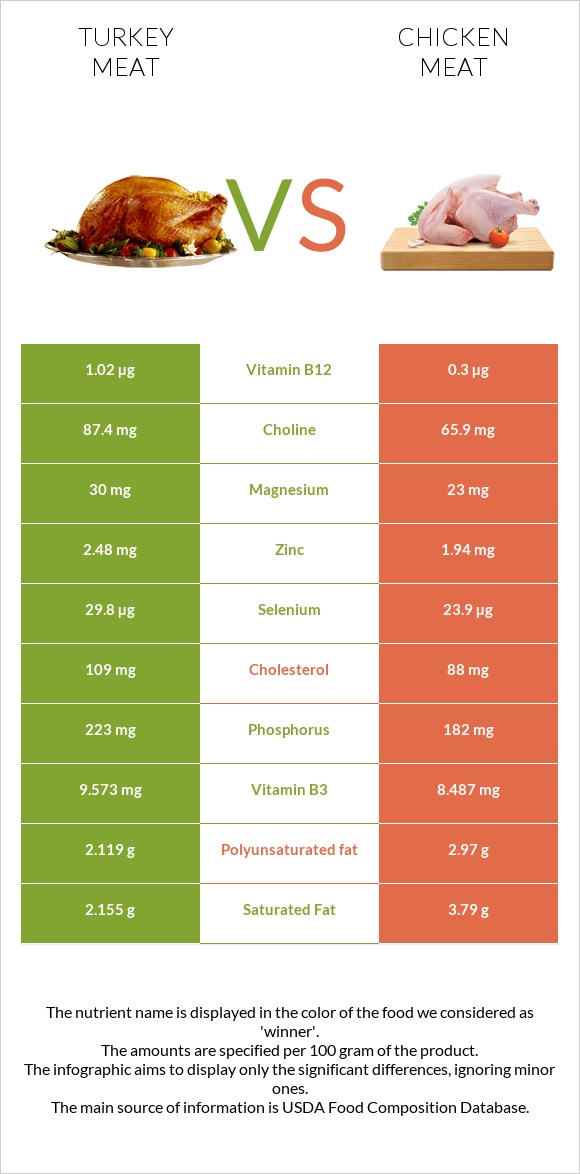
Summary
Chicken is higher in calories and fats, both saturated and polyunsaturated, while turkey is richer in protein and cholesterol.
Turkey is also richer in vitamins and minerals, such as magnesium, copper, vitamin B12, and folate. However, chicken has more vitamin A, vitamin E, and less sodium.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Classification
- Appearance
- Taste and Use
- Types of Meat
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients and Calories
- Calories
- Protein
- Fats
- Carbohydrates
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Glycemic Index
- Acidity
- Weight Loss & Diets
- Health Impact
- Health Benefits
- Cardiovascular Health
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Downsides and Risks
- Cardiovascular Health
- Cancer
- References
Introduction
Turkey and chicken meat have many things in common, both being white meat and poultry. However, these two kinds of meat have numerous differences as well. So, which is the right choice, and under which circumstances?
In this article, we will be comparing turkey meat with chicken meat with the main focus on nutrition and health impact.
Classification
Poultry meat is the meat of domesticated birds, such as turkey and chicken. Poultry meat is considered to be white meat, while the meat of mammals is classified as red meat.
White meat is naturally lighter in color due to a lower content of myoglobin, and therefore, a lower content of iron bound to it.
Appearance
Based on appearance, a whole turkey tends to be larger in size and the meat darker in color compared to chicken.
The leg meat of both turkey and chicken tends to be darker, while the breast and wing meat is lighter. This is due to the fact that both of these birds are flightless and walk instead; therefore, the muscles of the legs are better developed.
Taste and Use
While these two foods are usually said to have similar tastes, the flavor of turkey is often described to be more intense. However, surprisingly, one study found turkey meat to taste more like pork than chicken, describing the taste of both pork and turkey as fatty, salty, sweet, and umami (1).
Due to its larger size, turkey meat needs more seasoning and a longer time to cook.
The USDA recommends that all poultry, including turkey and chicken meat, be cooked at a minimum internal temperature of 165ºF or 74ºC (2).
Chicken is much more commonly consumed throughout the year, while turkey meat is often considered festive and is cooked on special occasions, such as Thanksgiving and Christmas.
Types of Meat
Many characteristics of the meat can vary depending on the age or sex of the animal, the conditions it was kept in, and other aspects.
Turkey and chicken meat can be used in their fresh or processed forms. However, processed chicken is much more popular compared to processed turkey.
Based on the method of raising the chicken or the turkey, they can be domesticated or wild.
Based on the cut of the meat, both turkey and chicken can be divided into three main parts: the breast, the wing, and the leg.
According to the USDA classification, based on the animal's age and weight, chickens can be classified into four groups: Cornish game hen, broiler-fryer, roaster, and capon.
Similarly, four classes of turkey have been defined based on the age and extent of breastbone calcification: fryer-roaster, young, yearling, and mature or old turkey, hen, or tom (3).
Nutrition
Based on many aspects, such as the cut, the age of the animal, and the cooking method, the nutritional values of these two kinds of meat can vary.
The nutritional values below are presented for a roasted whole turkey with meat and skin and a roasted chicken broiler or fryer with meat and skin.
Macronutrients and Calories
Chicken meat is overall denser in nutrients, containing nearly 60% water and 40% nutrients, while turkey meat consists of 64% water and 36% nutrients.
As stated by the FDA's Reference Amounts Customarily Consumed, the average serving sizes for these two types of meat per one person are as follows: one cup of chopped or diced chicken, weighing 140g and 3oz for turkey, equal to 85g.
As you can see, while being less dense in nutrients, the average serving size of turkey is much smaller when compared to that of chicken.
Calories
Both turkey and chicken are high-calorie foods; however, chicken contains notably more calories. Per a 100g serving, chicken has 50 more calories.
In an equal 100g serving of these foods, chicken provides 239 calories, while turkey meat contains 189 calories.
That being said, different parts of poultry contain different amounts of calories. The most calories can be found in the wing meat, followed by the legs. Consequently, the breast meat of chicken and turkey contains the least calories.
Chicken breast and wings provide more calories. However, turkey legs are higher in calories compared to chicken legs.
The calorie content found in a 100g of chicken breast is equal to 197, while turkey breast contains 189 calories (4, 5). The same serving size of chicken legs provides 184 calories, whereas turkey legs contain 208 calories (6, 7). And lastly, the same 100g serving size of chicken and turkey wings contains 254 and 229 calories, respectively (8, 9).
Protein
Poultry meat, such as chicken or turkey, is one of the best sources of protein.
While both of these types of meat are incredibly rich in protein, turkey provides more of it per serving. Turkey falls in the top 6% of foods as a source of protein. At the same time, chicken meat falls in the top 8% of foods as a source of protein.
In a 100g serving, turkey contains 28.5g of protein, while chicken provides 27.3g of it.
The protein founds in both of these meats is of very high quality, containing large amounts of all essential amino acids. Turkey and chicken are particularly high in tryptophan, lysine, and histidine. A 100g serving of these foods provides more than the needed daily intake value of these amino acids.
Compared to turkey, chicken meat has notably lower levels of isoleucine and valine.
Of these two types of meat, turkey is the better choice as a source of protein.
Fats
Chicken is significantly higher in fats when compared to turkey, unlike with protein. 13.6g of fats can be found in a 100g serving of chicken, while the same serving size of turkey meat contains only 7.39g of fats.
While being significantly higher in fats overall, chicken meat is only slightly richer when comparing polyunsaturated fatty acid content. Chicken meat provides more than two times more monounsaturated fatty acids.
As expected, turkey meat is lower in saturated fat content.
Both chicken and turkey are high in cholesterol. However, despite being higher in fats, chicken is lower in cholesterol. The same 100g serving of turkey provides 109g of cholesterol, while chicken contains 88g of cholesterol.
It is important to note that removing the skin before eating chicken or turkey reduces fat content intake significantly. However, according to the Harvard School of Public Health, most of the fat found in chicken skin is healthy, unsaturated fat (10).
Carbohydrates
Like most meat, turkey and chicken do not contain notable amounts of carbohydrates.
Chicken contains 0.06g of carbohydrates, while turkey has no carbohydrates at all.
Vitamins
Meat is an excellent source of a good many vitamins, especially the B complex vitamins.
Both turkey and chicken meat are incredibly rich in vitamins B3, B5, and B6. However, turkey is notably richer in vitamin B3 and vitamin B6, while chicken meat is only slightly higher in vitamin B5.
Turkey provides almost 2.5 times more vitamin B12. Turkey meat is also richer in vitamin B2 and folate. Turkey contains a decent amount of vitamin D, which chicken lacks.
On the other hand, chicken contains vitamin K, which is not found in turkey meat. Chicken meat is also almost 3 times richer in vitamin A and vitamin E.
Both turkey and chicken meat completely lack vitamin C.
Overall, turkey is richer in a greater number of vitamins compared to chicken.
Vitamin Comparison
Vitamin comparison score is based on the number of vitamins by which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" chart below show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food
![]()
6
:
5
![]()
Contains more Vitamin D +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B2 +67.3%
Contains more Vitamin B3 +12.8%
Contains more Vitamin B6 +54%
Contains more Folate +80%
Contains more Vitamin B12 +240%
Contains more Vitamin A +312.8%
Contains more Vitamin E +285.7%
Contains more Vitamin B1 +40%
Contains more Vitamin K +∞%
Equal in Vitamin B5 - 1.03
Contains more Vitamin D +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B2 +67.3%
Contains more Vitamin B3 +12.8%
Contains more Vitamin B6 +54%
Contains more Folate +80%
Contains more Vitamin B12 +240%
Contains more Vitamin A +312.8%
Contains more Vitamin E +285.7%
Contains more Vitamin B1 +40%
Contains more Vitamin K +∞%
Equal in Vitamin B5 - 1.03
Minerals
Turkey and chicken meat contain decent levels of all principal minerals.
Turkey is also richer in most minerals, containing larger amounts of magnesium, copper, zinc, phosphorus, selenium, and choline. Turkey is also somewhat higher in potassium.
On the other hand, chicken is slightly richer in iron, calcium, and manganese. Chicken is lower in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Mineral comparison score is based on the number of minerals by which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" chart below show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food
![]()
5
:
3
![]()
Contains more Magnesium +30.4%
Contains more Phosphorus +22.5%
Contains more Zinc +27.8%
Contains more Copper +40.9%
Contains more Iron +15.6%
Contains less Sodium -20.4%
Equal in Calcium - 15
Equal in Potassium - 223
Contains more Magnesium +30.4%
Contains more Phosphorus +22.5%
Contains more Zinc +27.8%
Contains more Copper +40.9%
Contains more Iron +15.6%
Contains less Sodium -20.4%
Equal in Calcium - 15
Equal in Potassium - 223
Glycemic Index
Due to the lack of carbohydrates, chicken and turkey meat are considered to have a glycemic index value equal to 0.
To read more about the glycemic index of foods with no carbohydrates, you can visit this page.
Acidity
The pH value of fresh chicken meat falls in the range of 5.8 to 6.3 (11). Turkey meat has been researched to have a very similar pH value in the range of 5.8 to 6.5 (12). Thus, the pH values of both chicken and turkey meat are slightly acidic.
Poultry meat has a pH value closer to neutral when fresh and gets more acidic over time (12).
When looking at these foods' Potential Renal Acid Load or PRAL values, turkey meat appears to be somewhat more acid-forming. The PRAL values for turkey and chicken are 16.3 and 14.6, respectively. The higher the positive PRAL value, the more acid the given food produces.
Weight Loss & Diets
Chicken and turkey meat can be considered to be high-calorie foods. However, between the two, turkey is the better option for low-calorie and low-fat diets.
Both turkey and chicken meat fit well into low-carb and low glycemic indeed diets, as these foods contain an insignificant amount of carbohydrates.
Along with a diet rich in vegetables, intake of poultry meat, such as chicken and turkey, has been correlated with a lower risk of developing extra fat and obesity (13).
Meat, especially poultry, is a great option as a source of healthy protein and fats on a keto diet.
Poultry meat is also recommended as part of the Mediterranean and Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, or DASH diets (14).
Health Impact
Health Benefits
As part of a vegetable-rich diet, consumption of poultry meat is associated with a risk reduction of developing overweight and obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Also, white meat, in particular poultry, is considered moderately protective or neutral on cancer risk (13).
In this section, we will further discuss the reasons behind these beneficial effects of white meat.
Cardiovascular Health
While intake of red or processed meat has been researched to be significantly associated with cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality, poultry intake is not (15). The substitution of one daily serving of red meat with a daily serving of poultry reduces cardiovascular risk by 19% (16).
These differences between red meat and poultry may be explained by the reduction of sodium, heme iron, and saturated fat intake. While turkey is lower than chicken in heme iron and saturated fat content, chicken has lower levels of sodium and cholesterol, as well as more polyunsaturated fat.
Diabetes
Recent studies have confirmed the existence of a link between hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance and the intake of saturated fat of animal origin (13). Although chicken meat is higher in saturated fat content, it is richer in healthy polyunsaturated fat as well.
Specific data concerning the consumption of poultry have confirmed the absence of a statistically significant relationship between an increasing weekly intake of chicken and turkey and the development of the disease (13).
When speaking of affecting the risk of developing diabetes type 2, it's not only the type of the product that matters but also the preparation method. Cooking meat at high temperatures, such as grilling and barbecuing, increases the risk of type 2 diabetes compared to cooking at moderate temperatures, such as boiling, steaming, and stir-frying (17).
If you'd like to read more about the effects of chicken meat intake on blood glucose levels, you can visit this page.
Cancer
White meat consumption is said to have a protective or neutral effect on the risk of various cancers.
A review of the literature confirms the inverse association between the number of poultry servings per week and the risk of esophageal carcinoma (13).
In order to decrease the risk of esophagus, liver, colon, rectum, anus, lung, pleura, and breast cancer, the substitution of red meat with white meat is recommended (18, 13).
Downsides and Risks
Cardiovascular Health
Even though the consumption of poultry is healthier than red meat when it comes to cardiovascular health, fish and vegetables may be the better options. Eating fish or vegetables instead of poultry has been studied to lead to a decreased risk of cardiovascular incidence (19).
Cancer
While fresh, cooked poultry may have a protective effect on tumors, the same cannot be said about processed chicken and turkey.
Processed meat intake can increase the risk of nasopharyngeal, esophageal, lung, stomach, and pancreatic cancer incidence (20).
Poultry consumption has also been positively associated with the risk of malignant melanoma, prostate cancer, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (21).
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221837180
- Cooking Meat? Check the New Recommended Temperatures
- https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/PoultryStandard.pdf
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171075/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171492/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173617/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171494/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173630/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171094/nutrients
- Ask the Expert: Healthy Fats
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/102/1/012051/pdf
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12835390
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462824/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322959346
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2759737
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16002829/
- How Meat Is Cooked May Affect Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3208759/
- https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/42/12/1136/6032616
- https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/meat-fish-and-dairy/
- https://jech.bmj.com/content/73/Suppl_1/A15.1
Infographic
Which food is preferable for your diet?
![]()
![]()
is better in case of low diet
 |  | |
| Low Fats diet | | |
| Low Carbs diet | | |
| Low Calories diet | | |
| Low glycemic index diet | Equal | |
People also compare
Vitamin and Mineral Summary Scores
The summary score is calculated by summing up the daily values contained in 300 grams of the product. Obviously the more the food fulfills human daily needs, the more the summary score is.
Vitamin Summary Score
50
![]()
36
![]()
Mineral Summary Score
37
![]()
31
![]()
Macronutrients Comparison
Macronutrient comparison charts compare the amount of protein, total fats, and total carbohydrates in 300 grams of the food. The displayed values show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of food.
Protein
171%
![]()
164%
![]()
Carbohydrates
0%
![]()
0%
![]()
Fats
34%
![]()
63%
![]()
Comparison summary
Which food is richer in minerals?
![]()
Turkey meat is relatively richer in minerals
Which food is lower in Saturated Fat?
![]()
Turkey meat is lower in Saturated Fat (difference - 1.635g)
Which food contains less Sodium?
![]()
Chicken meat contains less Sodium (difference - 21mg)
Which food is lower in Cholesterol?
![]()
Chicken meat is lower in Cholesterol (difference - 21mg)
Which food is cheaper?
![]()
Chicken meat is cheaper (difference - $1)
Which food contains less Sugar?
?
The foods are relatively equal in Sugar (0 g)
Which food is lower in glycemic index?
?
The foods have equal glycemic indexes (0)
Which food is richer in vitamins?
?
It cannot be stated which food is richer in vitamins. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts below for detailed information.
Source: https://foodstruct.com/compare/turkey-meat-vs-chicken-meat

0 Response to "Which Has the Most Protein Turkey Chicken or Beef"
Post a Comment